9.2. CDROM driver (sr or scd)
The SCSI upper level device name is "sr" while "sr_mod" is the module name. The device file name is either /dev/sr<n> or /dev/scd<n>.
Following is a diagram illustrating the CDROM subsystem of which sr is a part:
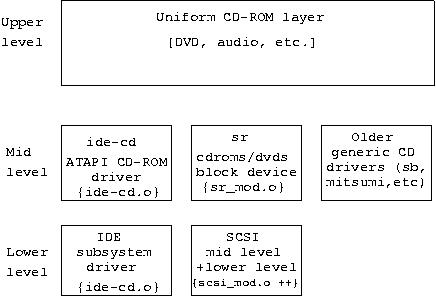
The architecture of the CD-ROM subsystem.
Many modern IDE CDROM players and all DVD players use the ATAPI standard which then allows them to be controlled by the SCSI subsystem with the ide-scsi lower level pseudo driver. The default action is for the IDE subsystem to take ownership of all IDE devices and in this case the default driver would be ide-cd.o . Once the IDE subsystem "owns" an ATAPI CDROM player then this excludes the ide-scsi driver from attaching itself to the same device. In order to change this default action see the following sections on boot and module parameters.
9.2.1. sr boot parameters
None but the following is related: During the boot sequence of the Linux kernel, the IDE devices are scanned before SCSI devices. This means that if both the ide-cd and ide-scsi drivers are built in, then the ide-cd driver will claim all CDROM devices on the IDE bus(-es). To override this action use the boot parameter "hd<x>=scsi" where <x> is the appropriate drive letter. In this case when the ide-scsi driver is initialized it will find the unclaimed IDE device and "claim" it for the SCSI subsystem.
9.2.2. sr module parameters
Doing a test to find out if a cdrom drive supports XA mode (mode 2) triggers firmware bugs on some drives. Consequently the check for XA mode support is turned off by default. The following module parameter is provided:
xa_test=<0|1> |
Continuing on with the ATAPI CDROM driver override discussion: for modules this can also be done with insmod ide-cd ignore=hdb to exclude that device. Typically the ide-cd module is loaded automatically so a line in the /etc/modules.conf file like:
options ide-cd ignore=hdb |
9.2.3. sr proc interface
All the following files are readable by all and produce ASCII output when read:
/proc/sys/dev/cdrom/autoclose /proc/sys/dev/cdrom/autoeject /proc/sys/dev/cdrom/check_media /proc/sys/dev/cdrom/debug /proc/sys/dev/cdrom/info /proc/sys/dev/cdrom/lock |
As an example, the auto eject feature can be turned on by the superuser with the command echo "1" > /proc/sys/dev/cdrom/autoeject. This will cause cdroms to be ejected from the drive when unmounted.